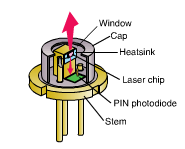
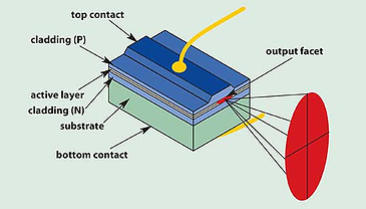
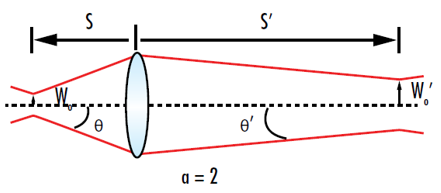
Laser Diodes for Gas Sensing: Mode-Hop-Free Tunability With High SMSR
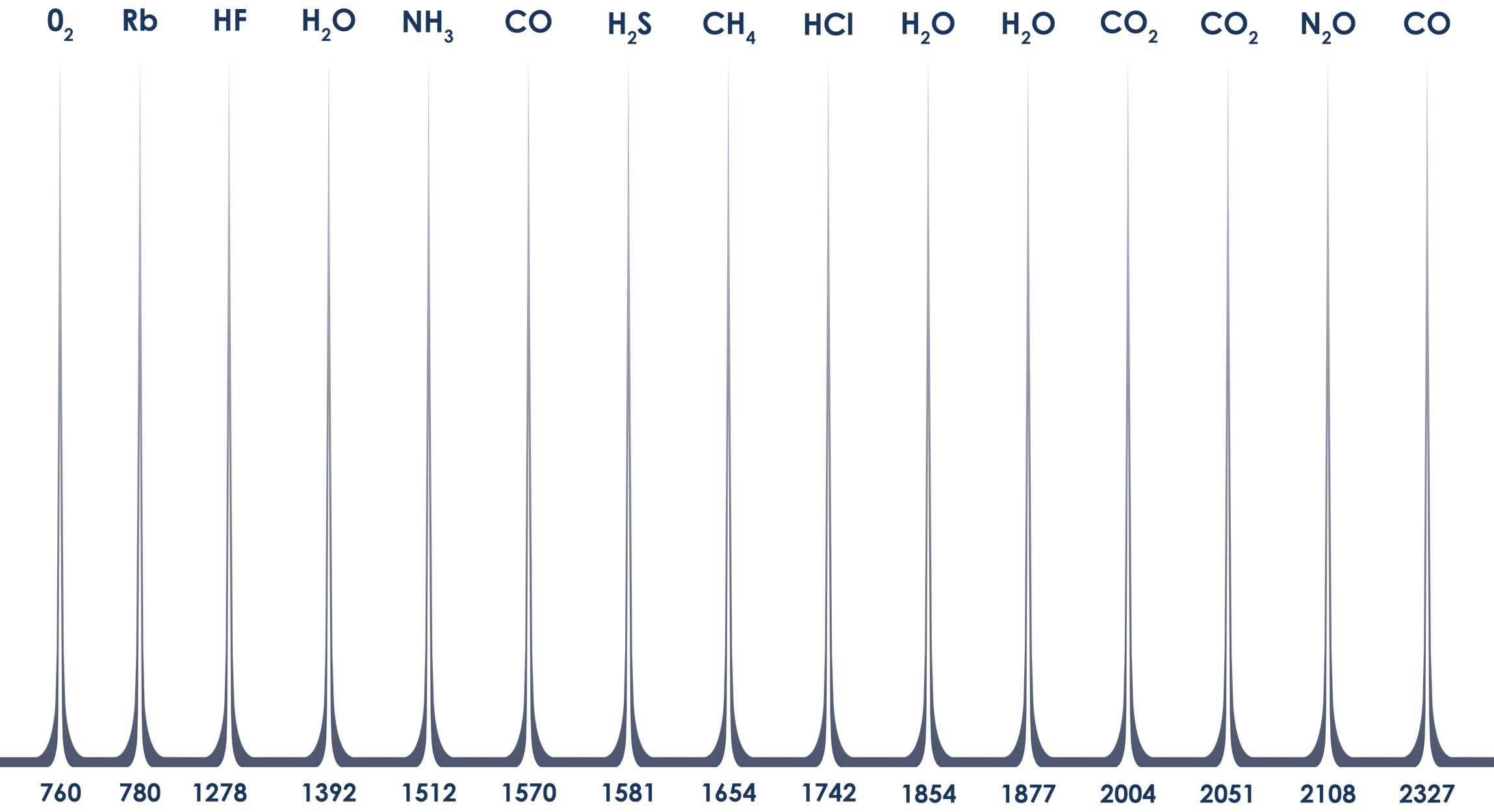
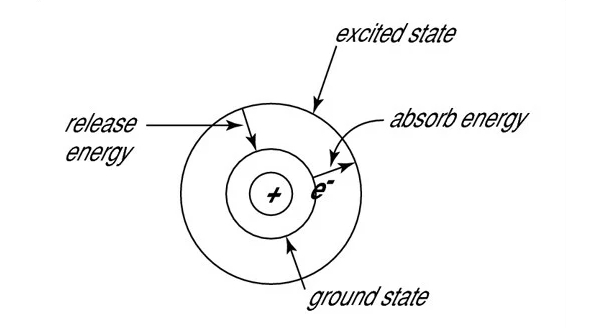
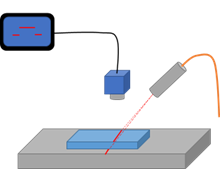
Single-frequency lasers have long been the cornerstone of standoff gas detection applications, particularly in traditional LIDAR (Light Detection And Ranging), DIAL (Differential Absorption LIDAR), and TDLAS (Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy) applications, where the sample needs to be accurately measured. More recently, as single-frequency laser diodes have become more common and less expensive, with a larger measurement range and compact size, they are being utilized in more localized and industrial gas sensing app… Read More

 BUY NOW
BUY NOW