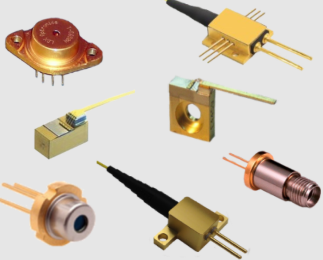
LDX Optronics: High-Power Multimode Laser Diodes for Precision Applications
For over three decades, LDX Optronics has delivered high-power multimode laser diodes, powering cutting-edge applications in Medical, Defense, and Industrial sectors. As RPMC Lasers’ exclusive North American partner, LDX offers an unmatched range of wavelengths (400–1900 nm) and power levels (up to 40 W), with industry-leading packaging expertise. This article explores LDX’s diode solutions, their applications, and how to select the right laser for your needs, spotlighting the LDX Optronics portfolio for superior pe… Read More

 BUY NOW
BUY NOW